Visual Raid
Simulates RAID Drives

Camboard Technology
Computer science software for k12 and ks3 computing curriculum..
Key Features
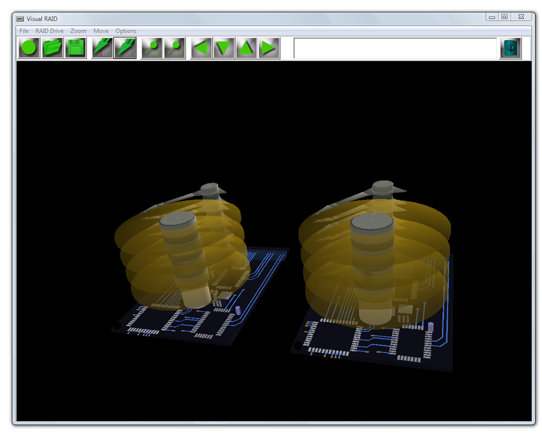
Simulates a RAID drive
Computer science software for k12 curriculum. Visual RAID simulates the operation of a servers dual RAID hard disk drives. Each virtual drive has a controller board, four magnetic platters and eight read/write heads. Upto 32 bits of data can be written and read from the RAID drive. The drive simulates data being written and read from the top platter. Virtual data can be written in a safe environment.
Read/Write to Virtual drive
Data can be read from the virtual disk and be displayed as binary, bytes and ASCII. How does RAID work RAID drives are used in servers. The principal reason for having a second hard disk is to have an exact replica of the data from RAID drive 1. If for any reason one of the RAID drives breaks down, data will be still intact on the other drive. RAID stands for redundant array of independent disks. So when data is being written it is sent to both RAID drives at the same time. When data is being read it is only read in from one RAID drive. In Visual RAID data is read in from Drive 1.
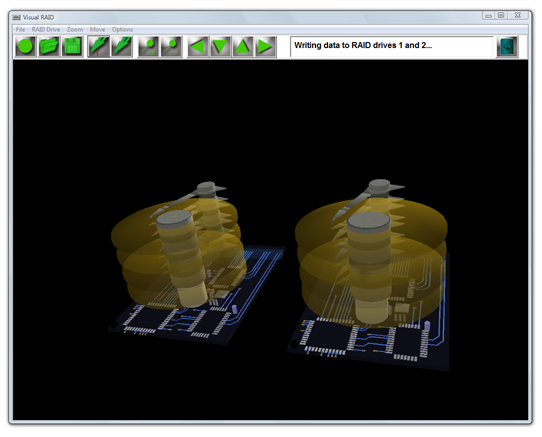
Data limits
Our hard drive is fixed to write at sector 1 from here we can write 32 bits of data. In total 32 bits of data can be written to the diskS. The program simulates data being written to sector 1. The start address is 0000000200 Addresses are offset from this start address. Write to disk Every part of the platter has its own unique capability to store a binary 0 or binary 1 when writing to the platter the magnetic surface will contain either 0 or 1. In our simulation a red dot signifies a 0 a gap signifies a binary 1. As the disks are spinning all the time a circular data trail is left. Visual RAID simulates how RAID works.

System Requirements
Requires a PC or laptop
With Windows XP/VISTA/7/8/10 and DirectX 8.1 or higher.